.NET MAUI Developer Skills To Expect
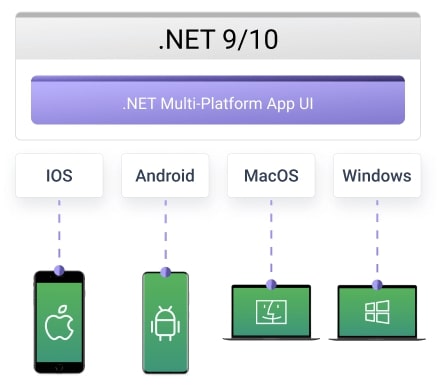
.NET MAUI lets one C#/XAML codebase deliver native apps to iOS, Android, Windows, and macOS. The unified, single-project model trims complexity, speeds releases, and cuts multi-platform costs while stable Visual Studio tooling, MAUI Community Toolkit, Telerik, Syncfusion, and Blazor-hybrid options boost UI power and reuse.
The payoff isn’t automatic: top MAUI developers still tailor code for platform quirks, squeeze performance, and plug into demanding back-ends and compliance regimes. Migration skills - code refactor, pipeline and test updates, handler architecture know-how - are in demand. Teams that can judge third-party dependencies, work around ecosystem gaps, and apply targeted native tweaks turn MAUI’s "write once, run anywhere" promise into fast, secure, and scalable products.
Belitsoft’s .NET MAUI developers create cross-platform apps that integrate cleanly with backend systems, scale securely, and adapt to modern needs like compliance, IoT, and AI.
Core Technical Proficiency
Modern MAUI work demands deep, modern .Net skills: async/await for a responsive UI, LINQ for data shaping, plus solid command of delegates, events, generics and disciplined memory management.
Developers need the full .NET BCL for shared logic, must grasp MAUI’s lifecycle, single-project layout and the different iOS, Android, Windows and macOS build paths, and should track .NET 9 gains such as faster Mac Catalyst/iOS builds, stronger AOT and tuned controls.
UI success hinges on fluent XAML - layouts, controls, bindings, styles, themes and resources - paired with mastery of built-in controls, StackLayout, Grid, AbsoluteLayout, FlexLayout, and navigation pages like ContentPage, FlyoutPage and NavigationPage.
Clean, testable code comes from MVVM (often with the Community Toolkit), optional MVU where it fits, and Clean Architecture’s separation and inversion principles. Finally, developers must pick the right NuGet helpers and UI suites (Telerik, Syncfusion) to weave data access, networking and advanced visuals into adaptive, device-spanning interfaces.
Cross-Platform Development Expertise
Experienced .NET MAUI developers rely on MAUI’s theming system for baseline consistency, then drop down to Handlers or platform code when a control needs Material flair on Android or Apple polish on iOS. Adaptive layouts reshape screens for phone, tablet, or desktop, while MAUI Essentials and targeted native code unlock GPS, sensors, secure storage, or any niche API.
Performance comes next: lazy-load data and views, flatten layouts, trim images, and watch for leaks, choose AOT on iOS for snappy launches and weigh JIT trade-offs on Android. Hot Reload speeds the loop, but final builds must be profiled and tuned.
BlazorWebView adds another twist - teams can drop web components straight into native UIs, sharing logic across the web, mobile, and desktop. As a result, the modern MAUI role increasingly blends classic mobile skills with Blazor-centric web know-how.
Modern Software Engineering Practices
A well-run cross-platform team integrates .NET MAUI into a single CI/CD pipeline - typically GitHub Actions, Azure DevOps, or Jenkins - that compiles, tests, and signs iOS, Android, Windows, and macOS builds in one go.
Docker images guarantee identical build agents, ending "works on my machine" while NuGet packaging pushes shared MAUI libraries and keeps app-store or enterprise shipments repeatable.
Unit tests (NUnit / xUnit) cover business logic and ViewModels, integration tests catch service wiring, and targeted Appium scripts exercise the top 20% of UI flows. Such automation has been shown to cut production bugs by roughly 85%.
Behind the scenes, Git with a clear branching model (like GitFlow) and disciplined pull-request reviews keep code changes orderly, and NuGet - used by more than 80% of .NET teams - locks dependency versions. Strict Semantic Versioning then guards against surprise breakages during upgrades, lowering deployment-failure rates.
Together, these practices turn frequent, multi-platform releases from a risk into a routine.
Security and Compliance Expertise
Security has to guide every .NET MAUI decision from the first line of code. Developers start with secure-coding basics - input validation, output encoding, tight error handling - and layer in strong authentication and authorization: MFA for the login journey, OAuth 2.0 or OpenID Connect for token flow, and platform-secure stores (Keychain, EncryptedSharedPreferences, Windows Credential Locker) for secrets.
All data moves under TLS and rests under AES, while dependencies are patched quickly because most breaches still exploit known library flaws. API endpoints demand the same discipline.
Regulated workloads raise the bar. HIPAA apps must encrypt PHI end-to-end and log every access, PCI-DSS code needs hardened networks, vulnerability scans and strict key rotation, GDPR calls for data-minimization, consent flows and erase-on-request logic, fintech projects add AML/KYC checks and continuous fraud monitoring.
Experience with Emerging Technologies
Modern .NET MAUI work pairs the app shell with smart services and connected devices.
Teams are expected to bring a working grasp of generative‑AI ideas
- how large or small language models behave, how the emerging Model Context Protocol feeds them context, and when to call ML.NET for on‑device or cloud‑hosted inference. With those pieces, developers can drop predictive analytics, chatbots, voice control, or workflow automation straight into the shared C# codebase.
The same apps must often talk to the physical world, so MAUI engineers should be fluent in IoT patterns and protocols such as MQTT or CoAP. They hook sensors and actuators to remote monitoring dashboards, collect and visualize live data, and push commands back to devices - all within the single‑project structure.
Problem-Solving and Adaptability
In 2025, .NET MAUI still throws the odd curveball - workload paths that shift, version clashes, Xcode hiccups on Apple builds, and Blazor-Hybrid quirks - so the real test of a developer is how quickly they can diagnose sluggish scrolling, memory leaks or Debug-versus-Release surprises and ship a practical workaround.
Skill requirements rise in levels.
A newcomer with up to two years’ experience should bring solid C# and XAML, basic MVVM and API skills, yet still lean on guidance for thornier platform bugs or design choices.
Mid-level engineers, roughly two to five years in, are expected to marry MVVM with clean architecture, tune cross-platform UIs, handle CI/CD and security basics, and solve most framework issues without help - dropping to native APIs when MAUI’s abstraction falls short.
Veterans with five years or more lead enterprise-scale designs, squeeze every platform for speed, manage deep native integrations and security, mentor the bench and steer MAUI strategy when the documentation ends and the edge-cases begin.
.NET MAUI Use Cases and Developer Capabilities by Industry
Healthcare .NET MAUI Use Cases
Healthcare teams already use .NET MAUI to deliver patient-facing portals that book appointments, surface lab results and records, exchange secure messages, and push educational content - all from one C#/XAML codebase that runs on iOS, Android, Windows tablets or kiosks, and macOS desktops.
The same foundation powers remote-patient-monitoring and telehealth apps that pair with BLE wearables for real-time vitals, enable video visits, and help manage chronic conditions, as well as clinician tools that streamline point-of-care data entry, surface current guidelines, coordinate schedules, and improve team communication. Native-UI layers keep these apps intuitive and accessible. MAUI Essentials unlock the camera for document scanning, offline storage smooths patchy connectivity, and biometric sensors support secure log-ins.
Developers of such solutions must encrypt PHI end-to-end, enforce MFA, granular roles, and audit trails, and follow HIPAA, HL7, and FHIR to the letter while handling versioned EHR/EMR APIs, error states, and secure data transfer.
Practical know-how with Syncfusion controls, device-SDK integrations, BLE protocols, and real-time stream processing is equally vital.
Finance .NET MAUI Use Cases
In finance, .NET MAUI powers four main app types.
Banks use it for cross-platform mobile apps that show balances, move money, pay bills, guide loan applications, and embed live chat.
Trading desks rely on MAUI’s native speed, data binding, and custom-chart controls to stream quotes, render advanced charts, and execute orders in real time.
Fintech start-ups build wallets, P2P lending portals, robo-advisers, and InsurTech tools on the same foundation, while payment-gateway fronts lean on MAUI for secure, branded checkout flows across mobile and desktop.
To succeed in this domain, teams must integrate WebSocket or SignalR feeds, Plaid aggregators, crypto or market-data APIs, and enforce PCI-DSS, AML/KYC, MFA, OAuth 2.0, and end-to-end encryption.
MAUI’s secure storage, crypto libraries, and biometric hooks help, but specialist knowledge of compliance, layered security, and AI-driven fraud or risk models is essential to keep transactions fast, data visualizations clear, and regulators satisfied.
Insurance .NET MAUI Use Cases
Mobile apps now let policyholders file a claim, attach photos or videos, watch the claim move through each step, and chat securely with the adjuster who handles it.
Field adjusters carry their own mobile tools, so they can see their caseload, record site findings, and finish claim paperwork while still on-site.
Agents use all-in-one apps to pull up client files, quote new coverage, gather underwriting details, and submit applications from wherever they are.
Self-service web and mobile portals give customers access to policy details, take premium payments, allow personal-data updates, and offer policy download.
Usage-based-insurance apps pair with in-car telematics or home IoT sensors to log real-world behavior, feeding pricing and risk models tailored to each user.
.NET MAUI delivers these apps on iOS, Android, and Windows tablets, taps the camera and GPS, works offline then syncs, keeps documents secure, hooks into core insurance and CRM systems, and can host AI for straight-through claims, fraud checks, or policy advice.
To build all this, developers must lock down data, meet GDPR and other laws, handle uploads and downloads safely, store and sync offline data (often with SQLite), connect to policy systems, payment gateways, and third-party data feeds, and know insurance workflows well enough to weave in AI for fraud, risk, and customer service.
Logistics & Supply Chain .NET MAUI Use Cases
Fleet-management apps built with .NET MAUI track trucks live on a map, pick faster routes, link drivers with dispatch, and remind teams about maintenance.
Warehouse inventory tools scan barcodes or RFID, guide picking and packing, watch stock levels, handle cycle counts, and log inbound goods.
Last-mile delivery apps steer drivers, capture e-signatures, photos, and timestamps as proof of drop-off, and push real-time status back to customers and dispatch.
Supply-chain visibility apps put every leg of a shipment on one screen, let partners manage orders, and keep everyone talking in the same mobile space.
.NET MAUI supports all of this: GPS and mapping for tracking and navigation, the camera for scanning and photo evidence, offline mode that syncs later, and cross-platform reach from phones to warehouse tablets. It plugs into WMS, TMS, ELD, and other logistics systems and streams live data to users.
Developers need sharp skills in native location services, geofencing, and mapping SDKs, barcode and RFID integration, SQLite storage and conflict-free syncing, real-time channels like SignalR, route-optimization math, API and EDI links to WMS/TMS/ELD platforms, and telematics feeds for speed, fuel, and engine diagnostics.
Manufacturing .NET MAUI Use Cases
On the shop floor, .NET MAUI powers mobile MES apps that show electronic work orders, log progress and material use, track OEE, and guide operators through quality checks - all in real time, even on tablets or handheld scanners.
Quality-control inspectors get focused MAUI apps to note defects, snap photos or video, follow digital checklists, and, when needed, talk to Bluetooth gauges.
Predictive-maintenance apps alert technicians to AI-flagged issues, surface live equipment-health data, serve up procedures, and let them close out jobs on the spot.
Field-service tools extend the same tech to off-line equipment, offering manuals, parts lists, service history, and full work-order management.
MAUI’s cross-platform reach covers Windows industrial PCs, Android tablets, and iOS/Android phones. It taps cameras for barcode scans, links to Bluetooth or RFID gear, works offline with auto-sync, and hooks into MES, SCADA, ERP, and IIoT back ends.
To build this, developers need OPC UA and other industrial-API chops, Bluetooth/NFC/Wi-Fi Direct skills, mobile dashboards for metrics and OEE, a grasp of production, QC, and maintenance flows, and the ability to surface AI-driven alerts so technicians can act before downtime hits - ideally with a lean-manufacturing mindset.
E-commerce & Retail .NET MAUI Use Cases
.NET MAUI lets retailers roll out tablet- or phone-based POS apps so associates can check out shoppers, take payments, look up stock, and update customer records anywhere on the floor.
The same framework powers sleek customer storefronts that show catalogs, enable secure checkout, track orders, and sync accounts across iOS, Android, and Windows.
Loyalty apps built with MAUI keep shoppers coming back by storing points, unlocking tiers, and pushing personalized offers through built-in notifications.
Clienteling tools give staff live inventory, rich product details, and AI-driven suggestions to serve shoppers better, while ops functions handle back-room tasks.
Under the hood, MAUI’s CollectionView, SwipeView, gradients, and custom styles create smooth, on-brand UIs. The camera scans barcodes, offline mode syncs later, and secure bridges link to Shopify, Magento, payment gateways, and loyalty engines.
Building this demands PCI-DSS expertise, payment-SDK experience (Stripe, PayPal, Adyen, Braintree), solid inventory-management know-how, and skill at weaving AI recommendation services into an intuitive, conversion-ready shopping journey.
Migration to MAUI
Every Xamarin.Forms app must move to MAUI now that support has ended: smart teams audit code, upgrade back-ends to .NET 8+, start a fresh single-project MAUI solution, carry over shared logic, redesign UIs, swap incompatible libraries, modernize CI/CD, and test each platform heavily. Tools such as .NET Upgrade Assistant speed the job but don’t remove the need for expert hands, and migration is best treated as a chance to refactor and boost performance rather than a port.
After go-live, disciplined workflows keep the promise of a single codebase from dissolving. Robust multi-platform CI/CD with layered automated tests, standardized tool versions, and Hot Reload shortens feedback loops - modular, feature-based architecture lets teams work in parallel. Yet native look, feel, and performance still demand platform-specific tweaks, extra testing, and budget for hidden cross-platform costs.
An upfront spend on CI/CD and test automation pays back in agility and lower long-run cost, especially as Azure back-ends and Blazor Hybrid blur lines between mobile, desktop, and web.
The shift is redefining "full-stack" MAUI roles: senior developers now need API, serverless, and web skills alongside mobile expertise, pushing companies toward teams that can own the entire stack.
How Belitsoft Can Help
Many firms racing to modern apps face three issues: migrating off end-of-life Xamarin, meeting strict performance + compliance targets, and stitching one secure codebase across iOS, Android, Windows, and macOS.
Belitsoft removes those roadblocks. Our MAUI team audits old Xamarin code, rewrites UIs, swaps out dead libraries, and rebuilds CI/CD so a single C#/XAML project ships fast and syncs offline, taps GPS, sensors, camera, and even embeds Blazor for shared desktop-web-mobile logic.
Our engineers land industry-grade features: HIPAA chat and biometric sign-on for healthcare, PCI-secure trading screens and KYC checks for finance, telematics-powered claims tools for insurers, GPS-routed fleet and warehouse scanners for logistics, MES, QC, and PdM apps with Bluetooth gauges for factories, and Stripe-ready POS, storefront, and AI-driven recommendation engines for retail.
Behind the scenes we supply scarce skills - MVVM/MVU patterns, Telerik/Syncfusion UI, AOT tuning, async pipelines, GitHub-/Azure-/Jenkins-based multi-OS builds, Appium tests, OAuth 2.0, MFA, TLS/AES, and GDPR/PCI/HIPAA playbooks - plus smart layers like chatbots, voice, predictive analytics, MQTT/CoAP sensor links, and on-device ML.
Belitsoft stays ahead of MAUI quirks, debugs handler-level issues, and enforces clean architecture, positioning itself as the security-first, AI-ready partner for cross-platform product futures.
Partner with Belitsoft for your .NET MAUI projects and use our expertise in .NET development to build secure, scalable, and cross-platform applications tailored to your industry needs. Our dedicated team assists you every step of the way. Contact us to discuss your needs.
Denis Perevalov
•
10
min read



 Profile us among companies that provide .NET development services. We propose a pilot project to get a feel for our benefits.
Profile us among companies that provide .NET development services. We propose a pilot project to get a feel for our benefits.











































.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
















We have been working for over 10 years and they have become our long-term technology partner. Any software development, programming, or design needs we have had, Belitsoft company has always been able to handle this for us.
Founder from ZensAI (Microsoft)/ formerly Elearningforce