Custom CRM Development Services
Custom CRM options by Belitsoft include custom CRM development from scratch if your workflows are exclusive and not supported by standard CRM platforms, and customization and modernization of your current CRM solution if the core functionality of the CRM software must be enhanced with custom features and modules to address missing capabilities.
Integrating AI into your CRM
- Predictive AI to identify deals' win-loss analysis and the best channels and messages
- Generative AI to create customized sales emails, knowledge articles, product descriptions and targeted marketing campaigns as well as craft AI-powered briefs summarizing past interactions with clients to establish context before making a call
- Conversational AI to interact with customers using agent chatbots trained on your own customer data (past interactions, service issue history, and contract details) hosted on your secure cloud platform
Custom CRM Solutions Development
Skilled CRM development team from Belitsoft creates custom CRM software tailored to your organization's structure and workflow, scalability needs, and branding guidelines. Belitsoft software development company is located offshore, which means cost-effective services compared to development costs in the USA, with the same or even better quality due to carefully vetted CRM developers who have formed the core of our team for the past 20 years. We automate business processes with CRM to optimize sales, marketing, and customer service.
CRM Customization
We create personalized CRM systems that include all the essential features found in enterprise-level CRM software. These platforms assist companies in reaching their customer retention objectives and enhancing sales performance. Our team of CRM developers uses the latest technologies to build bespoke CRM software solutions that can effectively reduce turnaround time.
CRM Mobile App Development
Our CRM app developers build bespoke mobile CRM apps to enable users to access features such as calendar, email creation and checking, account updates, video conferencing, dashboard & report viewing, and more. These features help businesses close deals more efficiently and provide faster support.
CRM Applications Development
Our technical experts leverage the latest industry technologies and programming languages to develop feature-rich custom CRM applications tailored to your business needs. We specialize in building top-notch CRM applications for all platforms, including web, desktop, and mobile.
CRM Business Analysis and Consulting
We provide comprehensive CRM development services that involve analyzing your industry and business requirements. Our team examines your business objectives and workflow to determine the most appropriate custom CRM development features to achieve excellent results. The aim is to maximize the benefits of your CRM development. To create the best CRM structure for your company, we conduct a thorough analysis of various factors, including your business operations, customers, their demand, industry type, and other relevant information.
Data Migration
Our custom CRM development company helps migrate your data safely and quickly if you've switched to a new CRM software. Our CRM system development services ensure they transmit your data from your current CRM to the new one with no loss or negative impact on your business efficiency. We transport your data safely, regardless of the system you are using to collect it, such as Excel or other tools.
Cloud-Based CRM Development
We develop cloud-based CRM solutions and offer easy installation of cloud-based CRM systems. This enables 24/7 access to critical client information from both the office and remote locations, ensuring that you keep in touch with your customers.
CRM Design
We understand the importance of creating a visually appealing and user-friendly customer relationship management system. Our design team prioritizes these aspects throughout the entire design process.
CRM Integration
Our team of custom CRM developers offers a secure integration of internal and external systems with your CRM, ensuring seamless and protected information flow. Your team turns out to be more efficient in managing data with automated processes while integrating all your systems, from data collection to analysis and forecasting.
Advantages of custom CRM development
Functionality choice option to correspond with your business workflow. Although CRM systems share the common feature of collecting and using customer data, companies' specific goals and desired functionalities may vary. Get a customer relationship management system to support unique business objectives.
A simple-to-use custom solution right for your specific needs and requirements vs. an expensive and complicated out-of-the-box enterprise CRM system, created to meet the requirements of most businesses. We build the functionality and user interface to minimize the learning curve for CRM users and encourage system adoption.
Significant cost-savings in the long run from the custom CRM development of those features you really need. With a CRM that ideally resolves your business tasks, you can achieve a higher lead conversion rate, faster customer service case resolution, and other positive outcomes.
Higher customer retention rates achieved with CRM, since it helps businesses ensure customer satisfaction: the customers feel valued and their needs are being met. This encourages building long-term relationships with them.
Increased sales results carried out as you track and analyze every step of the customer journey. Businesses can pinpoint areas to improve and optimize their sales tactics accordingly.
Higher activity effectiveness through custom CRM solutions. They enable businesses to streamline their processes and improve efficiency, resulting in significant savings of time, money, and resources.
Easy system scalability when new functionality is needed. Receive new features as required, rather than relying on a vendor to upgrade the platform on their schedule.
Ownership and total control over your custom CRM. You can grow your team without thinking of skyrocketing subscription fees.
Increased marketing results thanks to enabling businesses to target specific customer groups more accurately. This results in better marketing results, leading to increased business growth. This was proved by Belitsoft's case of building a Custom CRM Database for effective clinical trial recruitments.
Less time spent on training the end users because a customer relationship management system is created based on your workflow.
Better integration across different departments of your company. CRM applications for different departments, which are based on the same database and fulfill specific requirements of different company levels.
Features of a Custom CRM You Can Get
 Sales
Sales
A custom CRM boosts sales by enabling customer segmentation for personalized marketing, automating routine sales tasks for efficiency, and facilitating effective lead management to prioritize sales efforts. It provides comprehensive analytics and reporting, offering insights into sales performance and market trends, and aids in forecasting future sales. Importantly, a CRM enhances customer retention by offering superior service and personalized experiences, driving repeat sales which are more cost-effective than acquiring new customers.
 Pricing and billing
Pricing and billing
A custom CRM improves pricing and billing management by automating the invoicing process, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing the possibility of errors. It also maintains a comprehensive history of each customer's transactions, enabling swift identification of late or missing payments and a better understanding of customers' purchasing patterns. By integrating with existing accounting systems, the CRM facilitates real-time updates, ensuring all transactions are recorded accurately and promptly.
 Customer data management
Customer data management
Gather, store, and manage all customer-related data in a single, centralized location. By having a complete view of customer interactions and activities, organizations can improve customer engagement and enhance the customer experience.
 Lead capture
Lead capture
Save time and avoid manual lead registration by connecting CRM to all of your lead generation sources. Accurately collecting customer data can provide valuable insights for businesses to determine the actions of each customer segment and the stage in the customer lifecycle.
 Marketing
Marketing
Collect data to perform customer segmentation. It encourages them to create more targeted marketing campaigns and better understand and fulfill the needs of their customers. Effortlessly handle personalized campaigns triggered by events across a variety of marketing and advertising channels.
 Email and apps integrations
Email and apps integrations
Integrate your custom CRM solutions with email seamlessly by syncing your existing email channels, such as MS Outlook or Gmail with the CRM. This enables you to have full visibility of emails, contacts, calendars, and more across both desktop and mobile, supercharging your CRM platform. The integration with your ERP, financial software like Bookkeep, and others.
 Customer service
Customer service
Efficiently manage your contact center by implementing multi-channel case capture, rule-based case routing, and providing quick access to a comprehensive knowledge base for your agents.
 Customer self-service and feedback
Customer self-service and feedback
Establish a platform for customers to find custom CRM software solutions to frequently encountered challenges easily. It proceeds on the workload reduction of your customer service team. Create surveys to collect feedback and analyze customer sentiment in real-time.
 Partners tracking
Partners tracking
Collect and manage information about your partners. Improve customer experiences by keeping track of important details such as when, why, where, and how issues occurred. CRM enables you to monitor whether and how the issue has been resolved, providing valuable insights to improve your business productivity.
 Reporting
Reporting
Identify areas for optimization and facilitate data-driven business planning through the use of user-friendly records.
Why Choose Belitsoft Custom CRM Development Company
Hire a dedicated CRM software developer to get a customer relationship management system. Increase the number of customers and drive sales with it. While we are building a complex CRM system for your sales reps and managers and taking full responsibility for your customer relationship management optimization, you focus on the strategic goals of your future business development.
High-quality results. We develop quality software according to ISO 9001:2008 standards that meet all business goals. Belitsoft develops and delivers complete custom extensions with warranty terms.
Using the latest technologies. CRM experts apply innovative technologies, such as VoIP, RFID, and POS, to create tailored solutions that fulfill all of your business needs.
Industry-savvy CRM programmers with hands-on experience. Belitsoft has a well-versed team of professional software developers, QA engineers, business analysts, and project managers that build effective customized CRM systems on time and within budget. Our business analysts study all peculiarities of your business and provide an effective roadmap for custom CRM applications development, CRM integration, and upgrade. The CRM developers know the specifics of customer data processing and regulation in the industries like Healthcare, FinTech, eLearning, Logistics, Manufacturing, and many more.
Flexible forms of cooperation. Choose Belitsoft as your CRM development company and use flexible forms of cooperation and different dedicated team management models. Cut the costs of custom CRM development and its maintenance reasonably.
Ongoing maintenance. Besides deployment and customization, we offer ongoing maintenance service for the businesses running on CRM to provide timely system upgrades to address ever-changing market challenges.
Belitsoft’s Custom CRM Development Process

Discovery
- Our team examines your current processes that will the CRM will address, pinpointing manual workloads, challenges, and time-intensive tasks
- We discover areas for process optimization to enhance efficiency
- Our specialists conduct interviews and analyze business processes to understand your requirements for the CRM
- We determine both internal and external data sources for integration with the CRM
- Future CRM users are mapped out, including their role hierarchy and specific needs

CRM designing
- We develop usage scenarios for different user roles in the CRM
- Our team arranges the functional specifications of the CRM
- We create an integration plan for connecting the CRM to relevant systems and data sources
- Our team documents the architecture of the CRM, including the programming tools and technologies for each component
- We provide an estimation of the project timeline and cost

CRM development
- Our developers create all the CRM features, either by tailoring an existing platform or starting from scratch
- We establish APIs to connect the CRM with other systems you use
- Our team conducts comprehensive testing to evaluate CRM's functionality, integration, compatibility, security, and usability
- Once your CRM passes all tests, we proceed to launch it live

CRM testing and QA
- We enhance the security of your customer relationship management system and ensure maximum confidentiality by applying best practices of CRM development security

CRM support and maintenance
- We offer user training to facilitate smooth adoption of the CRM and address questions your team may have
- We provide L1-L3 support services upon demand
What Is The Cost of a Custom CRM?
If you're considering implementing a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system for your company, you can either choose an off-the-shelf solution or opt for a custom-built one.
Although custom CRM solutions can be expensive initially, it can spread out their benefits over a longer period. Most out-of-the-box CRM solutions have a per-user pricing model, and as your team grows, the costs will increase. You may require additional features and custom modules that come with higher monthly payments.
We realize the importance of selecting the right CRM solution for your business. Contact us to discuss your requirements and receive an approximate quote for the cost of developing custom CRM solutions.
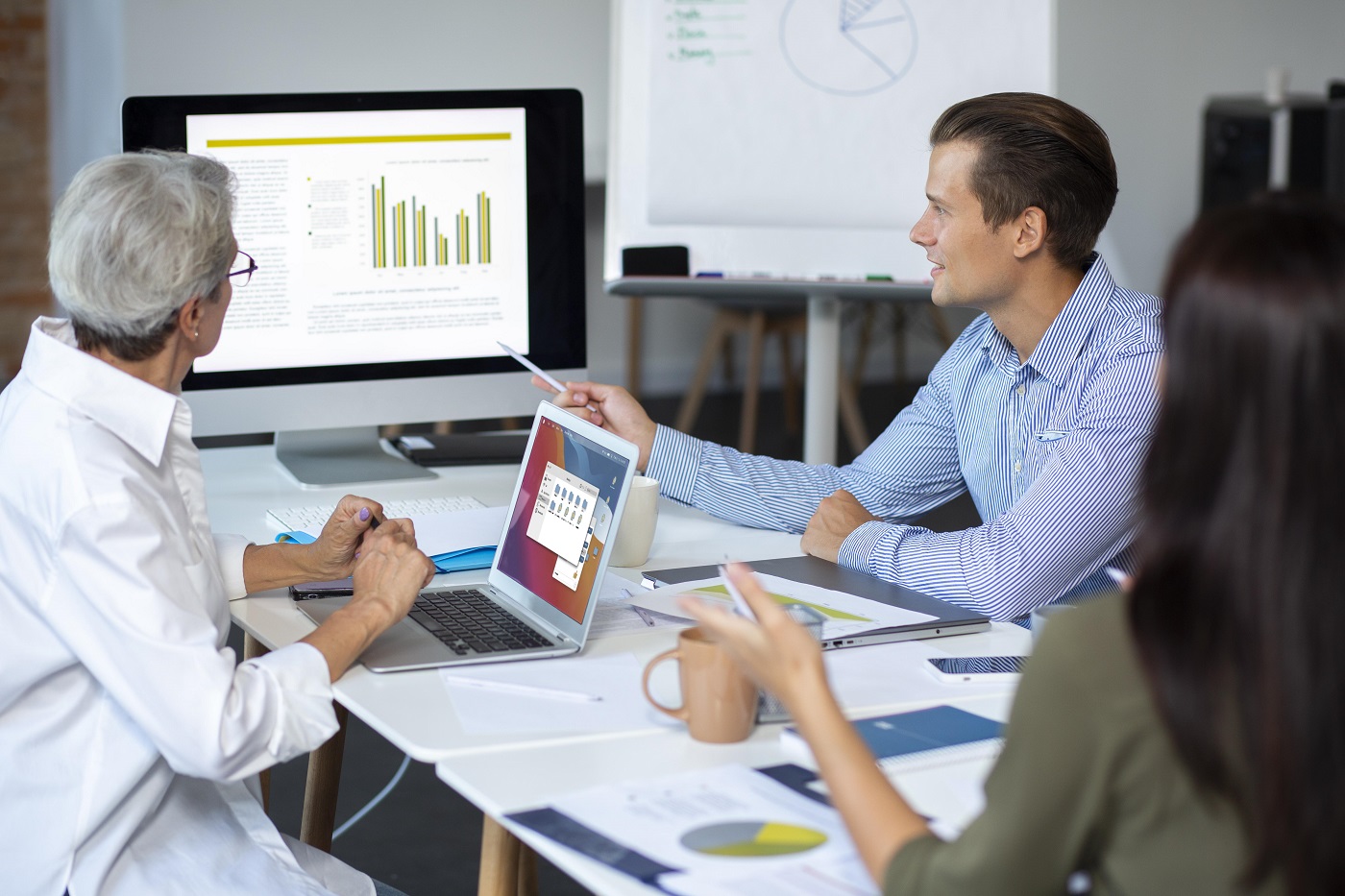
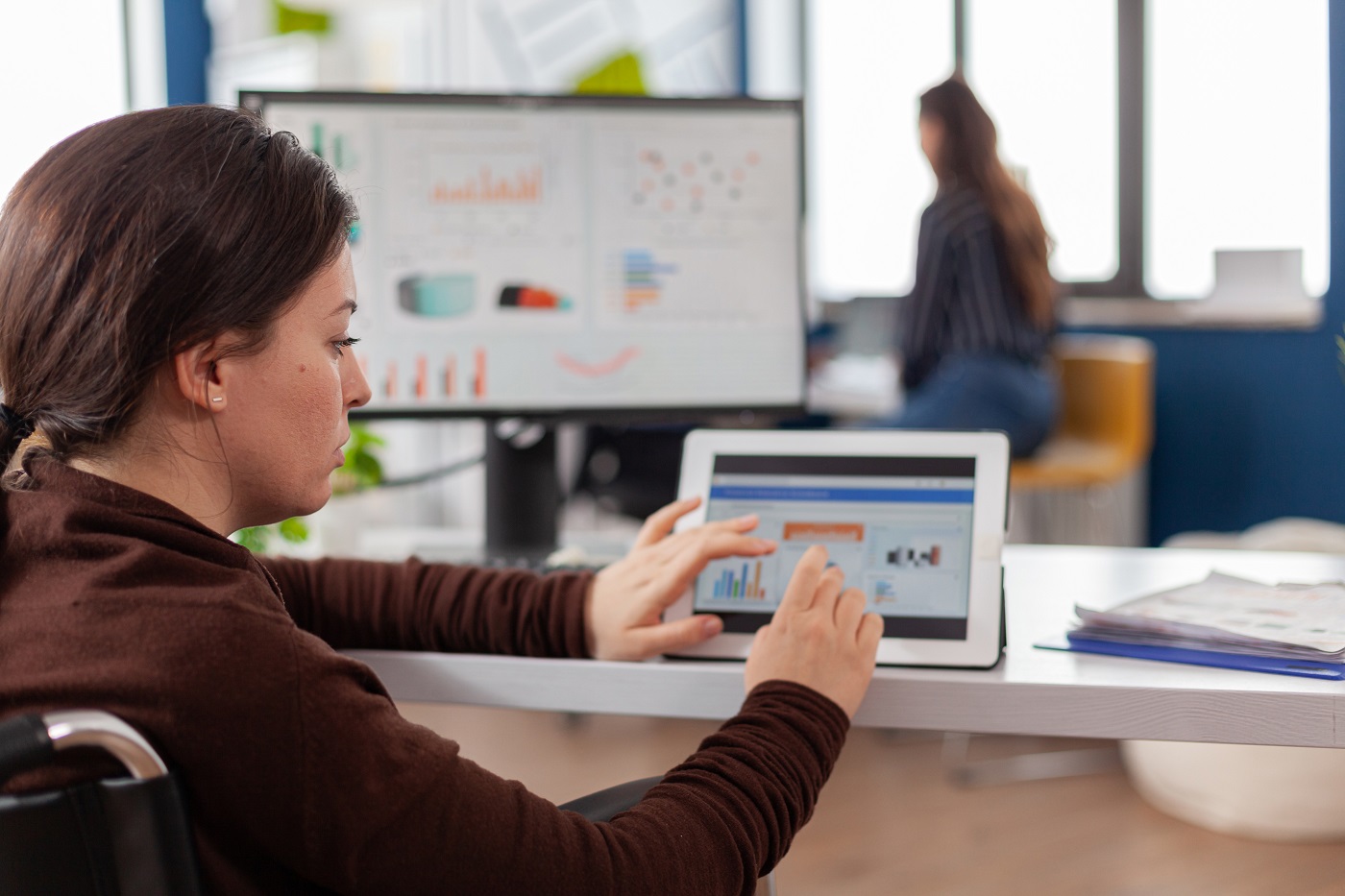


- When your business management has SugarCRM as a part of the software environment, we encourage you to use our SugarCRM development and maintenance services.
- To succeed, companies use effective customer relationship management. They adopt software like SugarCRM for better results. At Belitsoft, we offer integration services, custom SugarCRM app development, and maintenance.
- A fine-tuned software solution uniting all access points like PCs, mobile devices, other hardware, and middleware can grant productive end-to-end collaboration between executives, managers, customer service experts and other staff of a company. SugarCRM is an example of such solutions, therefore we choose it for customer management software development.
- We use Microsoft Dynamics development and integration for automation of business processes. You can make a dedicated team of professional developers at Belitsoft for implementation, integration, and support.
- Our applications simplify tracking your internal processes, help you make more accurate decisions, and speed up workflow. We delve into your operational details and involve professional designers for UI settings and .NET programmers for custom features - search, tracking, and modules.
- Whether you require additional features that are not available in CRM or ERP, we can help. Our team integrates Microsoft Dynamics products into your software environment and makes them fully compatible with your business goals and management processes through custom extensions or platform customization.
Belitsoft Works with Enterprises, Tech Companies, and Startups
At Belitsoft, we offer custom CRM development and customization of out-of-the-box solutions. Our team of developers builds a modern approach for managing your customer base, tailored to your business processes and goals. We provide a range of custom CRM development services from analysis to support and are experienced in various industries, including eLearning, Healthcare, Financial, Retail, Telecom, Logistics, and more.

- CRM development outsourcing
- Enterprise business automation
- Digital transformation
- Enterprise mobility
- CRM integration into other enterprise software

- Development team augmentation
- Product engineering
- Technology migration
- CRM maintenance and support

- Prototype designing
- MVP development
- Product engineering or reengineering
- CRM maintenance and support
- QA and software testing
Frequently Asked Questions
CRM systems are crucial for business success. They help identify and address customer needs, leading to stronger customer relationships. This results in increased loyalty and repeat business.
Implementing a custom CRM software can benefit your venture by:
- improving customer support
- increasing referrals
- organizing and identifying leads
- enhancing sales productivity
- boosting lead conversion rates
- elevating customer satisfaction
- facilitating decision-making
- increasing revenue
Incorporating CRM analytics into your custom CRM system allows you to gain deeper insights into customer behavior, market trends, and sales performance. This leads to further business growth and success.
Portfolio

Recommended posts
Our Clients' Feedback



















.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
![Integrate Your CRM with LMS to Increase Sales [Start now!]](/uploads/images/blog/posts/previews/image_162030700147-image(600x250-crop).jpg)
















We have been working for over 10 years and they have become our long-term technology partner. Any software development, programming, or design needs we have had, Belitsoft company has always been able to handle this for us.
Founder from ZensAI (Microsoft)/ formerly Elearningforce