Belitsoft stands out from other IT development companies by prioritizing healthcare software development. Benefit from 7+ years of our expertise in healthcare IT consulting services. Our medical software development company will help you decrease expenses on advanced technologies implementation, create a lucrative healthcare software product, or launch a cutting-edge IT initiative to streamline your business processes.
Create your technology strategy or launch/modernize your medical software with professional Healthcare IT consulting services from Belitsoft.
For almost a decade, Belitsoft’s healthcare IT consultants have been acting as reputable and trustworthy partners to medical organizations, pharmaceutical companies, healthcare startups, and medical device manufacturers. Our team has successfully fulfilled 10+ large projects (2000+ hours each).

Belitsoft as a Healthcare IT Consulting Firm

Healthcare IT Consulting Services
 Your current IT environment assessment
Your current IT environment assessment
 Healthcare IT strategy consulting
Healthcare IT strategy consulting
 Full-cycle IT consulting for medical solutions
Full-cycle IT consulting for medical solutions
 Digital health startup consulting
Digital health startup consulting
A Full Scale of Healthcare IT Services by Belitsoft
To ensure healthcare data security, seamless work of business processes, efficient resource allocation, and other benefits, Belitsoft offers a complete range of healthcare IT services. Our healthcare team has deep knowledge of advanced technologies, including Artificial Intelligence, IoT, blockchain, and others. We will help you both develop new healthcare software from scratch and improve your current solution.

Healthcare software development from scratch

Modernization and optimization of healthcare software

HIPAA-compliant cloud migration

Healthcare Software Integration

HIPAA compliance assessment & Healthcare cybersecurity

Healthcare IT support
Our 4-Step Medical IT Consulting Strategy
For software product companies, we carry out competitor research, market analysis, as well as identify target customers.
Then, our team gathers functional and non-functional requirements, specific healthcare software compliance requirements (for HIPAA, HITECH or other regulations) for further feature planning and prioritization.
Our experts recommend starting with MVP development if you need market validation or search for your first early stakeholders. It allows you to get a viable product with a simple UX/UI and key feature set. Upon validating your idea on the market and gaining stakeholders or investment, you simply keep on improving your software.
Healthcare IT Solutions from Belitsoft’s Experts
 Healthcare Data Management and Analytics Solutions
Healthcare Data Management and Analytics Solutions
Belitsoft’s IT consultants assist with integrating health data from various systems to give decision-makers valuable and data-driven insights about:
 Patient Engagement Solutions
Patient Engagement Solutions
Get professional help in planning and designing any patient-centered solution, including:
 Remote Patient Monitoring Solutions
Remote Patient Monitoring Solutions
Get expert advice on RPM software to be able to:
 Telemedicine software
Telemedicine software
Get advanced telemedicine software designed by Belitsoft’s healthcare IT team. You can get such functionality as:
 Digital Therapeutics & Chronic Care Management Software
Digital Therapeutics & Chronic Care Management Software
Benefit from Belitsoft´s expertise in designing healthcare software with the features, including but not limited to:
 Medical VR Software (Virtual Reality)
Medical VR Software (Virtual Reality)
Get expert advice on implementing VR software that will be highly helpful for:
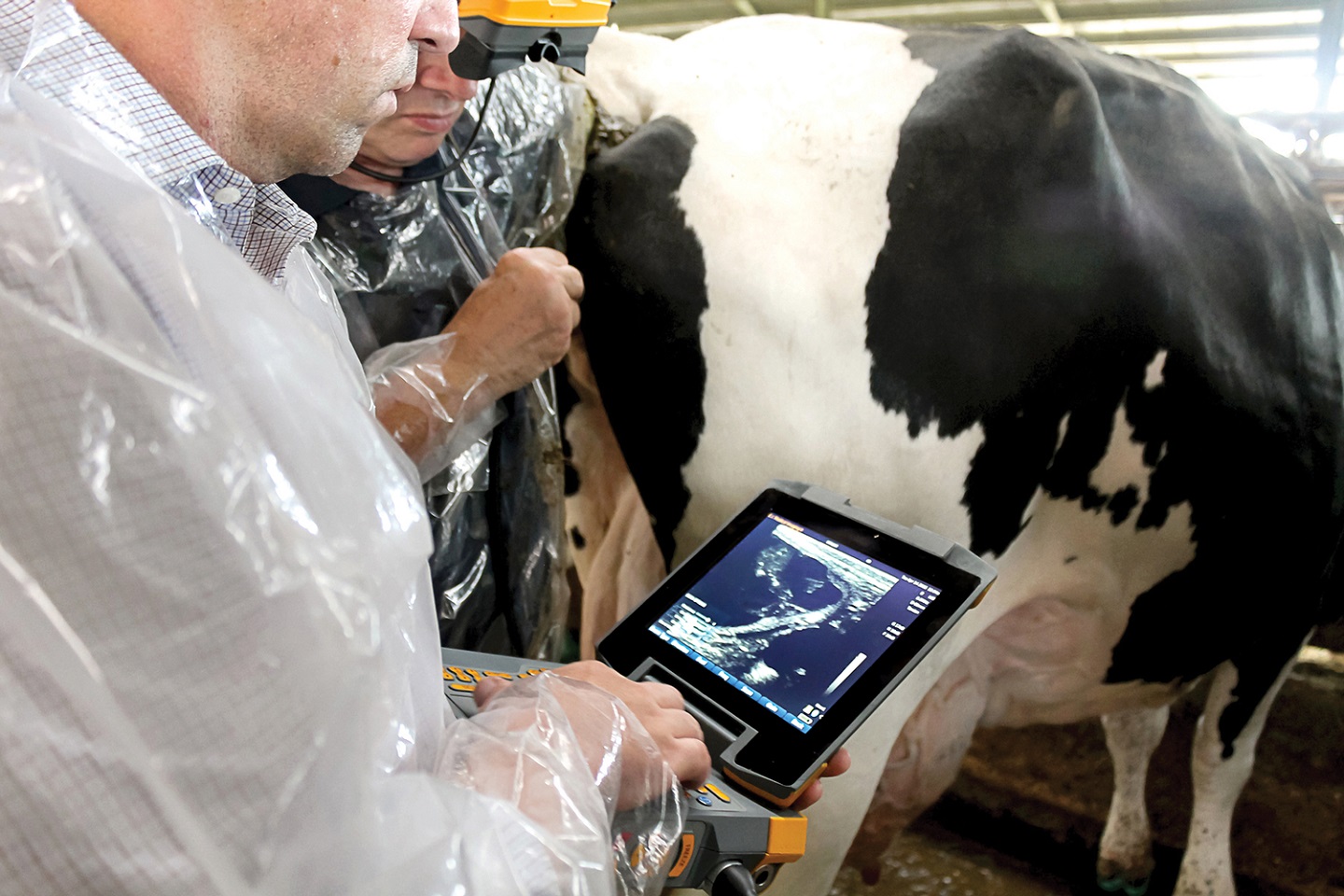
 Image Analysis Software
Image Analysis Software
Belitsoft consults and guides on implementing imagine analysis software for performing such tasks as:
 Digital Collaboration & Business Process Automation in Healthcare
Digital Collaboration & Business Process Automation in Healthcare
 Software as a Medical Device & Medical Device Software
Software as a Medical Device & Medical Device Software
Belitsoft helps seamlessly implement IoMT software by:
 Patient Relationship Management Software
Patient Relationship Management Software
Our healthcare IT consultants assist with:
Don’t see an ideal healthcare solution for your case? Share your ideas and needs with our healthcare IT consultants, and they will contact you back with a viable solution!
Healthcare IT Experts That Will Help You
Healthcare Department Head, Dzmitry Garbar
Deputy Business Development Director of Healthcare IT Consulting Team, Alex Shestel
Why Choose Healthcare IT Consulting Services from Belitsoft?
Years of Expertise in the Healthcare Industry
You will work with healthcare IT consultants that have expertise in health insurance, biotech and pharmaceutical domains, medical devices, clinical workflows, and other key aspects and segments of healthcare.
Full Scale of Healthcare IT Services
You will benefit from a one-stop-shop approach working with Belitsoft. Apart from healthcare software consulting services for software product companies and healthcare organizations, our team can help you develop custom software products, offer managed IT services, provide IT support, and overall implement your digital initiatives.
Quick Result Delivery and Early Benefits
You will get the MVP version of your software within several months. So you will start getting benefits from it, while we keep on adding further functionality and refining your product. Such an iterative approach permits us to bring better business results to healthcare organizations, pharmaceutical companies, healthcare software startups, and medical device companies.
Reduced development time and costs
You will save both time and money on healthcare software development with Belitsoft. We select suitable, proven software components, for example, cloud analytics services, to integrate them into a final product. On top of that, such an approach reduces the cost of ownership, helping you save in the long run.
Focus on Your Business Benefits
You can be sure that your medical IT solutions and healthcare software products designed with Belitsoft are backed by a well-thought business analysis. We focus on reaching KPIs, reducing IT operating costs, and enhancing clinical and business workflows, whether we work with software product companies or healthcare organizations.
Our Healthcare IT Consulting Services Improve Your KPIs
- Improve the quality of care and patient health outcomes, for example, decreasing the readmission rates and reducing complications rate.
- Enhance the performance of doctors, nurses, and other medical staff to ensure quicker patient care delivery and to reduce hours spent on routine manual work, such as creating reports.
- Minimize the cost of care, which focuses on reducing visit cost and ancillary expenses, as well as decreasing patient’s stay length in hospitals.
- Raise patient engagement through minimized hospitalization, higher visit attendance rate, and other means.
- Increase patient satisfaction, in particular, the number of patients that use your healthcare app on a daily basis.
- Improve medical asset management, which includes lower medical asset search time or higher asset utilization rate.
We Are Flexible in IT Project Pricing
We start with analyzing your healthcare project, budget, and other specifics to propose you the most optimal pricing model.

Choose this pricing model when you are likely to alter the functionality of your product during the healthcare software development, or you don’t know its final scope. In this case, you agree on an hourly rate for your dedicated developers and pay monthly, only for the time actually spent on your product.
Choose this pricing model when you prefer to have total control over the healthcare software development, and when the domain expertise of team members is critical to you. In this case, you make a monthly payment that includes the developers’ salary and the vendor’s overhead, covering insurance, utilities, and other expenses.


Choose this pricing model when the healthcare project scope is defined and clearly described in advance. In this case, a fixed quote is charged, and the payment is scheduled in accordance with the milestones of your project.
Portfolio


Recommended posts
Our Clients' Feedback





















.png)
.jpg)
.jpg)
















We have been working for over 10 years and they have become our long-term technology partner. Any software development, programming, or design needs we have had, Belitsoft company has always been able to handle this for us.
Founder from ZensAI (Microsoft)/ formerly Elearningforce