All the companies providing goods or services for the EU citizens will have to adhere to the new data protection rules or face fines of up to 4% annual global turnover or roughly $24.5M. As the GDPR comes into force it will affect businesses all over the world, including 52% of American firms. Established companies have already released statements claiming to have prepared for the new privacy rules. But Gartner predicts that only half of the businesses will succeed. We have prepared a list to help you be among them.
Protect your users' data and ensure GDPR compliance with this checklist. If you need help implementing these measures, let us know.
What is GDPR? Who needs to prepare for GDPR?
The acronym stands for General Data Protection Regulation. It is a legal document detailing the rules pertaining to personal information collection and processing. In contrast to the recommendation-like 1995 Data Protection Directive, GDPR is a binding legislative act.
According to the full text of GDPR, any organization which gathers or processes EU citizens’ personal data is subject to the regulation. Moreover, all your contractors (including software development companies) need to adhere to the standard for your app to be GDPR-compliant. Experts at Gartner think that the authorities would start enforcing the legislation right after it comes into effect, so the sooner you will be ready, the better.

The regulation and its accompanying documents are massive in scope and size (260 pages), but there are things you can do to make your product fit its requirements.
1. Get informed consent
Description
The GDPR states that the businesses now have to ask users to agree to collecting and processing their personal information. The request "must be given in an intelligible and easily accessible form, with the purpose for data processing attached to that consent”.
Your application has to describe what information will be handled, why and where. Silence or doing nothing doesn’t equal consent – the user has to take an action (like ticking the checkbox). A timely notification with a clear description and an option for the user to accept/decline will do the job.
Moreover, if you already have a certain user base, you might need to have them “repermission” your app, lest their consent level is below the GDPR-compliant.
User must take an action to confirm consent to processing their personal information (e.g. click on the "I agree" form). Withdrawing consent should be as easy.
- No expression of consent is needed if you ask for an information which is absolutely necessary to do your part of the agreement (e.g. full name and address for an online shop)
- If you want to use client's data for extra purposes (behavior analysis, advertising etc.) you have to ask for consent.
Tech. Solution
Include the consent withdrawal option in the user's profile.
The text of the consent request must be clear and unambiguous. The "I agree" tickbox will be enough, but the user must take an action to clearly express their will.
2. Data Minimization
Description
Store only the data that is necessary, delete when it is not needed anymore.
Make sure that you are collecting only the information you can’t do without. And, if possible, implement automatic deletion of the data you no longer need. This will both protect your users’ privacy (giving you another selling point) and help you avoid lots of trouble in case of a data breach: informing the authorities and the owners of affected accounts, as well as paying a huge fine for ignoring data minimization rules.
‘Where there is a reason to process the data, there is no problem. Where the reason ends, the processing should, too.’
Bart Willemsen, research director at Gartner
Solution
There are three main types of collected information:
- The necessary minimum data to do business (e.g. an online shop needs only the name and address of a person to deliver their goods);
- Extra data (sex, age, marital state) which isn't directly involved in company's service requires getting extra consent or justification in the public offer of your business;
- Sensitive personal data, which is often used for profiling (sexual orientation, political and religious views, race, ethnicity etc.) requires another expression of consent.
3. Personal data encryption
Description
Encryption adds an extra layer of security the hacker must defeat before they can access the information.
The GDPR Article 32 requires that the personal data is protected by the “state-of-the-art” measures. However, the exact nature of those measures is left for the companies to decide. As Belitsoft has quite a bit of experience in building HIPAA-compliant medical apps which have similar technical requirements, there are a few options we can recommend.
It goes without saying that the personal data must be encrypted. The Ashley Madison hack has shown that the company has stored the users’ addresses and credit card details in plain text, leading to multimillion-dollar lawsuits. If GDPR was in effect back then, the company would’ve also received a huge fine.
Tech. Solution
There are three main ways that you can approach the creation of the GDPR-compliant database.
First one is developing your own custom server with centralized database development. It will be able to provide the necessary level of security and saves you money in the long run, although you will need to make a certain investment up front. However, it will require careful optimization, as encrypting and decrypting information might be resource-intensive.
The second option is turning to the third-party GDPR-compliant server with centralized DB. It is a much quicker solution, as all the technical issues have already been solved by the provider. It is also cheaper in the short term (the associated development costs are relatively minor) but will cost more in the long run.
The third option is using blockchain technology and building custom server with a decentralized database. It is secure by design and will be considered a sufficient measure of protection. It is also a cost-effective long-term solution.
Data Encryption, Third Party Server.
Need a team of experts to build your GDPR-compliant application? Contact us and get a free quote on your project!
4. Implement "privacy by design" and "privacy by default"
The concept of “privacy by design” is somewhat uncertain, but boils down to making sure privacy is taken care of at every stage of the product’s lifecycle. Implementing this idea is a much larger undertaking, which may even lead you to rewrite your app from scratch. To start, you need to conduct a Privacy Impact Assessment to determine which functionality you need to implement or modify. After the results are in, it is a matter of using them to design the application in a way that keeps personal information safe.
‘Many of the companies who we're talking to… they're going to want to trade with Europe too, and therefore it's very important that they buy a platform that is going to be compliant with those regulations.’
Paul Clarke (CTO at Ocado) on GDPR
4.1 Two-Factor Authentication
Description
TFA protects from online fraud and identity theft
Tech. Solution
Integrate with Google Authenticator or similar service.
For iOS
For Android
4.2 Blocking brute force attacks
Description
If a hacker intends to use automated login/password guessing, these measures can stop them. More about Brute Force Attack
Tech. Solution
- Use Google Authenticator which can change access code every few seconds.
- Block account for several minutes after three failed login attempts
- Ask users to pass a CAPTCHA test after a certain number of failed logins.
4.3 Automatic Log-Off
Description
This feature helps prevent unauthorized access and modification of data
4.4 Separate domain names for Customer and Admin portals
Description
Separating portals helps protect the information and allows securing admin section without hampering users.
4.5 HTTP Authentication for Web Admin Panel
Description
Common CMS's have common vulnerabilities. This feature adds another layer of protection against them.
Tech. Solution
4.6 SSL Certificate
Description
SSL certificates protect the information transfer between app server and database or between the user and your service.
Tech. Solution
4.7 Locking Unused Database Ports
Description
New servers are shipped with all the ports open. Lock the unneeded ones so they can't be used for intrusion.
4.8 Database can be accessed only from API server IP
Description
Allowing only one IP-address will prevent unauthorised access and locate data breach. Cloud firewalls could help with that.
Tech. Solution
4.9 Database connects to API server via HTTPS
Description
Encryption helps protect the information while it is in transfer.
4.10 Server is accessed via VPN
Description
VPN adds another layer of security to the data on the server.
4.11 Regular Database backup
Description
Backup the information in the DB and store it on an external cloud service. In the event of data breach, it will help to minimize losses.
Tech. Solution
4.12 Regular Server Log Backup
Description
All the server logs should be kept and stored externally. It helps locate inconsistensies in case of hacker attacks.
Tech. Solution
4.13 Adjust Inotify
Description
Set up triggers and notifications to detect intrusion quickly.
Tech. Solution
4.14 Log all the Server Actions
Description
Logs allow to find out which data was modified.
“Privacy by default”
“Privacy by default” essentially means that if there are privacy settings in your product, they must be set to maximum at the start. Feel free to include an option to downscale the protection, should someone wish it. But your app cannot make a new user do something to get the highest level of privacy.
The Privacy by default options in the app should be set to maximum protection when a user first registers/installs the app.
Tech. Solution
- "Restrict private data usage" checkbox should be selected by default.
- Solution should pass "Data Protection Impact Assessments" (DPIA.)
Pseudonymization
Pseudonymization means storing information which can identify a person (e.g. social security number) and the related data (gender, age, location etc.) separately.
Tech. Solution
- System shouldn't collect data, which can allow matching user profile with real person without user consent;
- Private data should be stored on separate server with encrypted database;
- Application APIs should be covered by automated tests to prevent personal data leak
5. Prepare for the users exercising their rights
The new European regulation has given people extra rights that companies must grant: Right to be forgotten; Right to object; Right to rectification; Right to access; Right to portability.
.This calls for an update to your privacy policy, as well as the public offer of your product. In addition, giving every user an option to request correction, transfer or deletion of their data (even through a simple contact form) will be a must.
5.1 Right to be Forgotten
Description
Users can ask the company to delete all of their personal data if at least one of the following is true:
- Personal data is no longer needed for the stated purposes of processing;
- A person has withdrawn their consent and there is no other basis for the processing;
- Personal data has been acquired/processed illegally;
Tech. Solution
Manual removal of user data in private storage after receiving (for example by mail) request from a user.
5.2 Right to Object
Description
Users can object to using their personal data for direct marketing purposes, including profiling.
Company must clearly inform the user about this right at the first contact and stop this user's data processing after receiving an objection.
Tech. Solution
"Restrict private data usage" checkbox should be introduced to the user profile.
5.3 Right to Rectification
Description
- If their stored personal data is wrong, the user has the right to request its correction.
- Taking into account the purposes of the processing, the data subject shall have the right to have incomplete personal data completed, including by means of providing a supplementary statement.
Tech. Solution
Manual editing of data in private storage after receiving (for example by mail) a request from a user.
5.4 Right of Access
Description
Users have a right to know what information is stored.
Tech. Solution
This information should be presented to a user before registering in the system.
5.5 Right of Portability
Description
A user can ask to receive their personal data in a convenient format and request the transfer of their data to the other company (if technically feasible).
Tech. Solution
Implement the following:
- Automatic report generation to present private data in a convenient form;
- Manual removal of user data in private storage.
6. Document everything
The regulation requires companies to not only implement additional data protection measures but also document them to be able to prove that they’ve taken the necessary steps. Otherwise, the official audit will prove that the company is incompliant and – you’ve guessed it – must pay a fine.
That is why it is important to properly prepare security policies, data protection impact assessments, personal data registry and other relevant documents. See the complete list of things to describe on the Information Commissioner’s Office website.
This task of mapping out the information processing and putting it on paper usually falls to Data Protection Officer (it’s likely you’ll need one). If you don’t have such a specialist on staff, you might also be breaking the law and putting your business at risk.
7. Plan for contingencies
No matter how well you are defended at the moment, it pays to be prepared for personal data breaches.
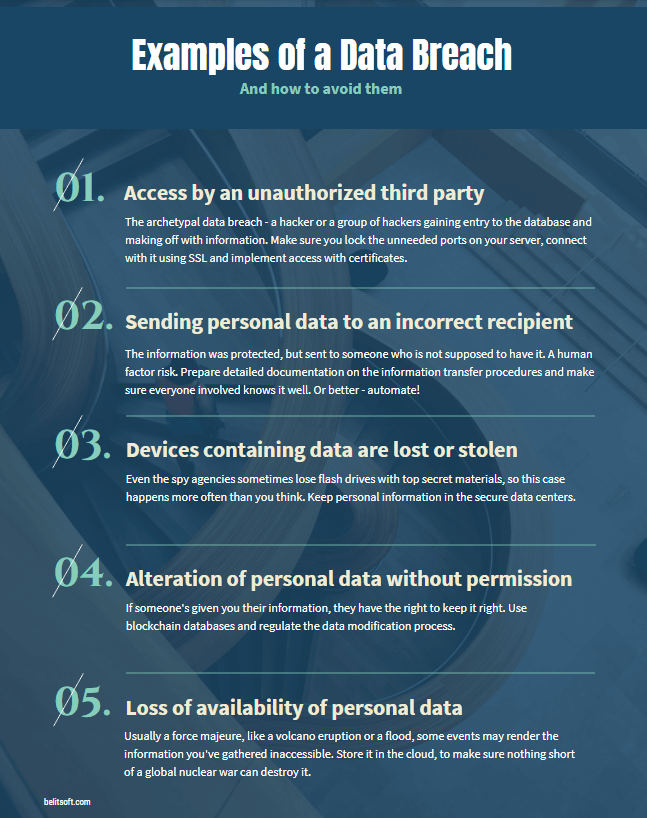
In most cases, you’ll need to notify the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) within 72 hours of detecting a breach. If you opt not to, you must have a valid (and properly supported by documents) reason for it. But if there is a “high risk to the rights and freedoms of individuals”, you need to inform your users as well.
The notification for users must be written in a clear and plain language and include the following:
- Name and contacts of your DPO (or another contact point, if you don’t have a Data Protection Officer);
- Description of the likely consequences of the data breach (costs, reputation damage and so forth);
- Measures you’ve taken or intend to take to mitigate the information leak.
If you fail to notify the ICO when necessary, the maximum fine might reach EUR 10M or 2% of annual global turnover. Note that this might stack with other fines, so having a reporting procedure in place is important.
Tech. Solution
Prepare a mass mailing plan for this contingency.
Rate this article
Recommended posts
Our Clients' Feedback

















.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)
.png)
.png)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.jpg)
















We have been working for over 10 years and they have become our long-term technology partner. Any software development, programming, or design needs we have had, Belitsoft company has always been able to handle this for us.
Founder from ZensAI (Microsoft)/ formerly Elearningforce