This article is a review of the most popular open source EHRs. The recommendations inside are based on the 4+ years of experience we have in developing and customizing EMR/EHR systems for hospitals, private practices and physicians, outpatient facilities, pharmacies, medical software businesses and EHR startups from USA and Europe. The review describes the products, gives an overview of their features, Meaningful Use/Promoting Interoperability eligibility, risk of being vendor-locked, as well as user reviews and advantages and disadvantages of each.
✅ What is an open source EHR?
Open source EHR is a fully functioning EHR/EMR system that you can start to implement today for free.
Open source software is software with freely available source code. Unlike proprietary software, anyone can modify and distribute the code without licensing fees, as defined in the software’s license.
The term “open source” does not imply that the data in an open source system is available to anyone. In fact, many argue that open source systems are safer than proprietary systems.
Open source software generally provides greater flexibility to select and switch vendors and make changes to the software.
Various successful open source health information technology and EHR projects exist and should be evaluated before creating a system or purchasing a proprietary system.
Key Similarities and Differences between Open Source and Proprietary EHRs
Similarities (same for both systems)
- Require planning before implementation (cost estimation, processes standardization, etc.).
- Require implementation (software customization, training of personnel, server setup, etc.).
- Require maintenance after implementation (software, creating and training new users, etc.).
- Require data and information security measures to prevent data leaks and other IT security threats.
- Require a legal framework (patient data confidentiality, security, interoperability, etc.).
Differences
Open source EHRs:
- Client can make improvements independent of vendor.
- Client can implement it without vendor.
- Client can use system if vendor contract ends.
- Client can look and try out system before implementation without vendor assistance.
- Client can get service from many vendors.
- Client can add functionality through source code updates and modifications.
Proprietary EHRs:
- Company that owns software decides who can provide services, such as implementation or support.
- Client is unable to improve or update software until vendor releases a new version.
- Client may need vendor support to implement/customize functionality.
- Vendor may limit free trials to a few days.
- Vendor have multitude of business licensing models with variability in subscription terms and maintenance.
In general, Open Source Software provides more power and options to the customer because the customer owns not only its own data, but also the system itself, which has many advantages.
Advantages of Open Source EHRs:
- Very easy to acquire and test before implementation.
- Less vendor lock, meaning they aren’t required to use the EHR vendor for all changes to the system.
- More control over data.
- Reduced development and configuration costs.
- Increased interoperability. Most solutions include open and international standards.
Reduced Vendor Lock
Because modifications to an EHR system tend to be complex, many vendors of proprietary EHRs are known for charging high fees for this work, increasing their fees once the system has been implemented, or providing poor service. With an open source EHR system, the customer can choose whether to use a vendor or internal IT people to modify the system. If a vendor is chosen, the customer has more control over the vendor because the customer can change vendors without also losing the system. That said, given the complexities of maintaining a functioning EHR system, changing vendors is not easy either. For example, there may not be another vendor in the region for the system, or customizations or missing documentation would make changing vendors difficult. Despite these constraints, the use of open source EHRs provides more leverage to hospitals, governments, and other consumers in a market that is highly controlled by EHR companies.
This is even more important for national or regional implementations where a Ministry of Health, for example, chooses a single system and by default creates a regulatory monopoly. If the system is not open source, the cost of changing the system is so high that the vendor is practically irreplaceable. There have been many cases of vendors using this position to their favor. As an example, consider the situation if two countries implement a national EHR system, with Country A using a proprietary system and Country B using open source tools to build their own. Country A has to pay the vendor for each update, and only the vendor can modify the functionality. As a result, Country A has to pay any fee set by the vendor. Country B is able to change or update its EHR system according to its budget and can use a vendor or an in-house IT team to make modifications.
Increased Control of Data
Customers of open source systems can have more say and control over how the data are stored and used. This facilitates, for example, the development or use of complementary programs to access that data for in-house reporting.
A problem that arises frequently in proprietary EHR systems is that the customer lacks control of features, such as reporting functions, in the system. This was the case, where health centers had to pay every month to get their monthly report with updated data. A similar problem is that proprietary EHR customers cannot change the content of the report even if it is discovered that the report no longer fits the client’s needs.
With open source EHR, a customer can modify functionality independent of the vendor to extract and view their data. So if the customer wants to examine specific data to determine how to better meet patients’ need or other purposes, the customer has the option of doing it themselves and not necessarily rely on the vendor as with many proprietary systems. All of this, however, is dependent on the customer having the appropriate technical access to their system.
Reduced Developmental Costs and Flexibility to Expand
Given that open source EHR is free to download and try for any length of time and proprietary software, if the vendor allows, often has short test periods, open source EHR systems have less risk. Furthermore, if the open source system has many organizations continually improving it by developing it, then the customer may get that additional functionality without having to pay for its development. Additionally, open source EHR systems have the benefit of allowing the customer to choose who builds additional functionality for them, so they are not bound to their current vendor.
EHR systems are complex and have a high failure rate, but they are also an essential part of the workflow. Because of this, chang- ing EHR systems is expensive and getting it right the first time is difficult. Thus, organizations should want to have a system that they can modify and expand with as little cost as possible and a vendor who is flexible. Both of these occur more easily with open source EHR systems. To modify the system, for example, if the code is open source, the customer has options as to who develops it whether internally, through their vendor, or another vendor. Also, given that the customer has more options and is not locked into a contract with one vendor, the vendor has to be more flexible.
Increased Interoperability
Though both open and proprietary systems can use open standards, open source systems are more likely to use these standards. This is, in part, because people who work with OSS systems tend to be in favor of open standards, whereas proprie- tary vendors have a commercial interest in keeping clients from changing to another system. Proprietary vendors therefore tend to be wary of open standards. A review paper found that proprietary issues were in the top three reasons for lack of interoperability, after privacy and sustainability.
Building your own EHR
If your organization has decided to build its own EHR system or have its IT staff provide technical support for a system that will be built, using an open source EHR system as a starting point is the most logical choice. Most, if not all, open source EHR systems have already established the basic functionality required for a good system. This includes creating users, permissions, and reports. Additionally, many have created flexible frameworks to customize the system to the needs of the organization. In ge- neral, these functionalities have been tested over many years by different organizations to ensure they work, and it is harder to justify the expense involved in recreating them for the new system. For example, OpenMRS has spent at least US$8 million creating its system, and that money does not need to be spent again to reinvent the wheel.
✅ What are the top 3 Open Source EHR systems?
There are over 30 open source EHR systems worldwide such as OpenEMR, Docmein, HealthKit, ERPNext, OpenMRS, one touch emr, FreeMED, GNU Health, Vista EHR, Bahmni, HospitalRun, CottageMed, OpenClinic, WorldVistA, GNUmed, FreeMedForms, ZEPRS, LibreHealth EHR, DoliMed EMR, nosh EMR, Care2x, EncounterPRO, Caisis, Solismed, RemoteClinic and more. Some systems were designed for specific countries, such as OSCAR for Canada, OpenMAXIMS and Ripple for the United Kingdom. Others are focused on specific medical specialties, such as Open Dental for dentists, Odoo Medical for primary care, and OpenEyes for ophthalmology. Here we review the systems designed for worldwide use.
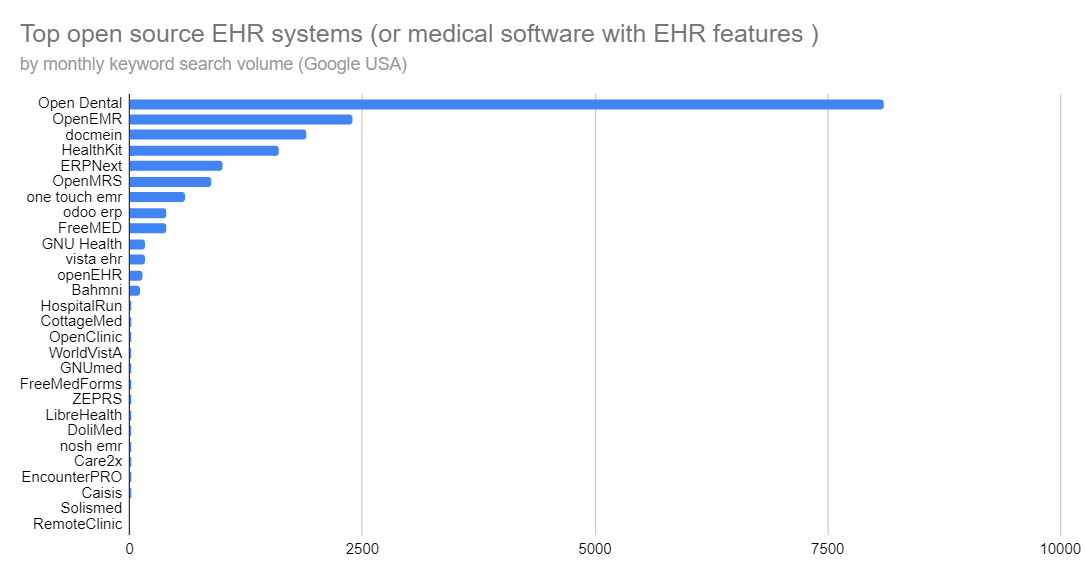 Top open source EHR systems (or medical software with EHR features) by monthly keyword search volume (Google USA, Semrush). Source: https://belitsoft.com/
Top open source EHR systems (or medical software with EHR features) by monthly keyword search volume (Google USA, Semrush). Source: https://belitsoft.com/We have chosen three universal EHR system (OpenEHR, OpenEMR, and OpenMRS), and one speciality-specific EHR (OpenDental) for the following reasons:
- There is the demand for these systems.
- These systems are built using the most popular programming languages.
- These systems are mostly HIPAA/GDPR compliant.
- Some of these systems have ONC certification.
1. OpenEMR: Universal EHR
An extremely popular free EHR/Practice Management software, reaching up to 3000 downloads per month, OpenEMR is much more than just a barebones record store. It has all the major features expected of an EHR:
OpenEMR Core Features
HIPAA compliance
Compliance with the HIPAA requirements is a must for any EHR. Achieving it requires securing several parts, which include OpenEMR itself, servers (Apache, MySQL, PHP), and network (firewall, router, https, certificates, etc). OpenEMR developers make it a priority to keep OpenEMR updated with the most recent security options.
Belitsoft specializes in delivering easy to manage HIPAA-compliant solutions and technology services for medical practices of all sizes. Contact us if you would like to get a HIPAA risk assessment and analysis.
Access control is the first Technical Safeguard Standard of the HIPAA Security Rules. Assigning roles to different EHR users helps to delineate their access to the information/pages/options according to their positions. That will ensure the patients’ data will only be accessible to the authorized employees. The Administrator of an OpenEMR instance can add users to a set of appropriate user access groups.
EHR Interoperability standards support (HL7 FHIR)
OpenEMR provides Basic FHIR EHR Interoperability standard support that allows to export/import all the patient data about patients in RESTful API format. OpenEMR also provides Basic FHIR Support using SMART on FHIR implementation or HAPI FHIR implementation to integrate EHRs with other health IT systems.
Meaningful Use Stage 3 Compliance
OpenEMR Version 5.0 is compliant with 2014 Edition CEHRT. The current version of OpenEMR (5.0.2) partially satisfies the criteria of 2015 Edition CEHRT, and the OpenEMR development team is working to meet the new requirements without referring to specific timelines.
Remote access
The OpenEMR software suite is a web-based application that allows users to access patient data from any computer.
Mobile compatibility
Users are able to access OpenEMR via mobile devices, both on Android (up to v9) and iOS (up to v12). The usability of pages could be constrained by the screen size, so the user would have to work in a landscape mode to ensure the best performance.
Other features:
- Medical Records with demographics, vitals, FHIR/CCDA compatibility, and even voice recognition;
- Scheduling, with multiple facilities support, SMS/email notifications, messaging system and more;
- E-prescribing, including pharmacy dispensary module;
- Billing, including flexible coding system, claims management, insurance tracking etc.;
- Clinical decision rules;
- Reporting, including sales, prescriptions, referrals and more;
- Patient portal and a secure API (Application Programming Interface) to integrate third-party portals.
OpenEMR is written in PHP, one of the most popular programming languages. This gives you a wide array of options when choosing a company to customize the system for your practice, because there are many developers who have been working with this technology for years. It is also well-documented, which makes customization easier for the programmers and cheaper for the practice.
Another thing worth mentioning is that OpenEMR is distributed under GNU GPL (General Public License).
The reviews of OpenEMR are mostly positive. Judging by what the users say, its advantages are:
- Low cost of ownership;
- High speed;
- Many customization options;
- User-friendly interface;
- Free technical support;
However, there are drawbacks too:
- The practice needs an in-house IT team or an outside vendor to customize OpenEMR and support it;
- Lack of learning resources for end users;
- Support is often slow to respond;
- Billing and insurance modules need extra work;
- Additional customization is required for specialty practices (e.g. Orthopedics or Mental Health).
2. OpenMRS: Universal EHR
This system is a relative newcomer to the EHR/EMR market. Since its inception in 2004 it has been in use all over the world, including the United States.
While OpenMRS is mainly a foundation to build a full-fledged EHR upon, its reference web-application already provides many features “out-of-the-box”, for example:
- Web-Based EHR: this web application can run on your own servers or in the cloud (e.g. AWS);
- Medical Records (Patient repository): a medical records store with demographics, encounter data etc.;
- Scheduling: processing and managing appointments and provider schedules;
- Patient workflows: entering patients into clinical programs and tracking their recovery through each stage of that program;
- Reporting, a system of customizable reports;
- Security, including authentication and role-based access;
- HL7 support: ability to import HL7-formatted data;
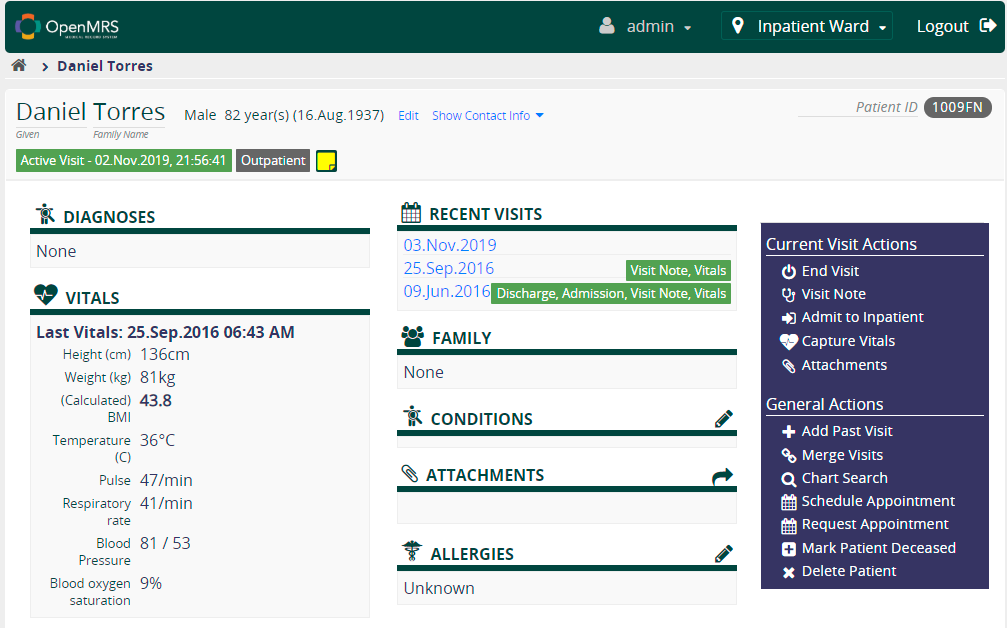 OpenMRS's Active Visits Dashboard. Source: openmrs.org/demo/
OpenMRS's Active Visits Dashboard. Source: openmrs.org/demo/OpenMRS is written in Java, the most popular programming languages.
OpenMRS has modular architecture and offers a number of add-ons to customize the system to your practice’s workflows and requirements.
As OpenMRS was mostly intended to be used outside of the USA, it is not ONC-certified by default. However, with a competent development company at your side, you can build your own EHR system that satisfies the ONC criteria and gets the verification needed to participate in the incentive program.
There are few reliable reviews of OpenMRS, but the users consider it easy to use, praise its price (or lack thereof) and enjoy the control over the records it gives. However, they also note that it is hard to set up without programming knowledge and lacks mobile apps.
OpenMRS is a free EHR. It is distributed under Mozilla 2.0 license.
3. OpenEHR: Universal EHR
OpenEHR is a set of specifications and tools for making custom medical software. EtherCIS is the leading open source implementation of the openEHR standard in action. It is a clinical data repository that consolidates data from various clinical sources, such as an EMR or a lab system, to provide a full picture of the care a patient has received.
OpenEHR uses Java, PHP, and JavaScript, which are all popular languages. Which means there is less chance of becoming vendor-locked when using a custom system - there are many companies working with these languages.
The specifications and source code for OpenEHR can be downloaded for free. However, some assembly is required before you can have an EHR/EMR of your own. This could be done either by your in-house IT-team or by a custom software company. In either case, this is a cost to be included in your budget.
OpenEHR is distributed under Apache 2 license.
Why not VistA EHR
VistA is being in the service of the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) since the late 70’s. Under the Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) most of its source code was released as public domain, which prompted companies and development teams to create derivative systems, also known as distributions: OSEHRA VistA, OpenVistA, WorldVistA and others.
As there are many versions on the market, describing the features of each would take too long. However, there are core functions shared by the most popular ones:
- Health information (patient records), including diagnoses, vitals, allergies etc.;
- Scheduling;
- e-Prescribing;
- Billing;
- Clinical decision support;
- Electronic communication (messaging);
- Patient support, e.g. patient portal or educational materials;
- Reporting and population health, for example, immunization reports.
Some distributions, like OSEHRA VistA, can be downloaded for free. Others are paid.
The default version available to the general public, FOIA-VistA, is not ONC certified. Some of its code has been redacted pre-release, so many features don’t work as planned. The popular OSEHRA VistA has most Meaningful Use criteria fulfilled, but doesn’t have official verification. However, a number of distributions, do have certification.
VistA might seem outdated, however it gets a lot of praise from its users for functionality, speed and security. The different distributions of it, though, haven’t gathered many public reviews.
VistA and its distributions are primarily written in MUMPS or M - a programming language, used mainly by companies working in the Healthcare domain, like EPIC, Medicare and Allscripts.
It is rather rare - SourceForge, a major open source community, has only 37 MUMPS projects, compared to over 54.000 Java or 34.000+ PHP counterparts. This means that there is only a limited pool of development companies to choose from for implementation and customization, leaving you in danger of becoming vendor-locked.
As mentioned previously, VistA is a public domain software. However, its distributions use different licenses. For example, WorldVista is covered by GPL, while vxVistA 15.0 is under Apache 2.0.
4. OpenDental: a Specialty-Specific EHR
Formerly known as “Free Dental,” OpenDental is a specialized practice management/EHR system for dental health clinics. It is used both in the USA and abroad: in Australia, the Netherlands, etc.
The full function version of OpenDental is only available under the commercial license because it includes royalty bearing, licensed materials from the American Dental Association (ADA), the Code on Dental Procedures and Nomenclature (CDT).
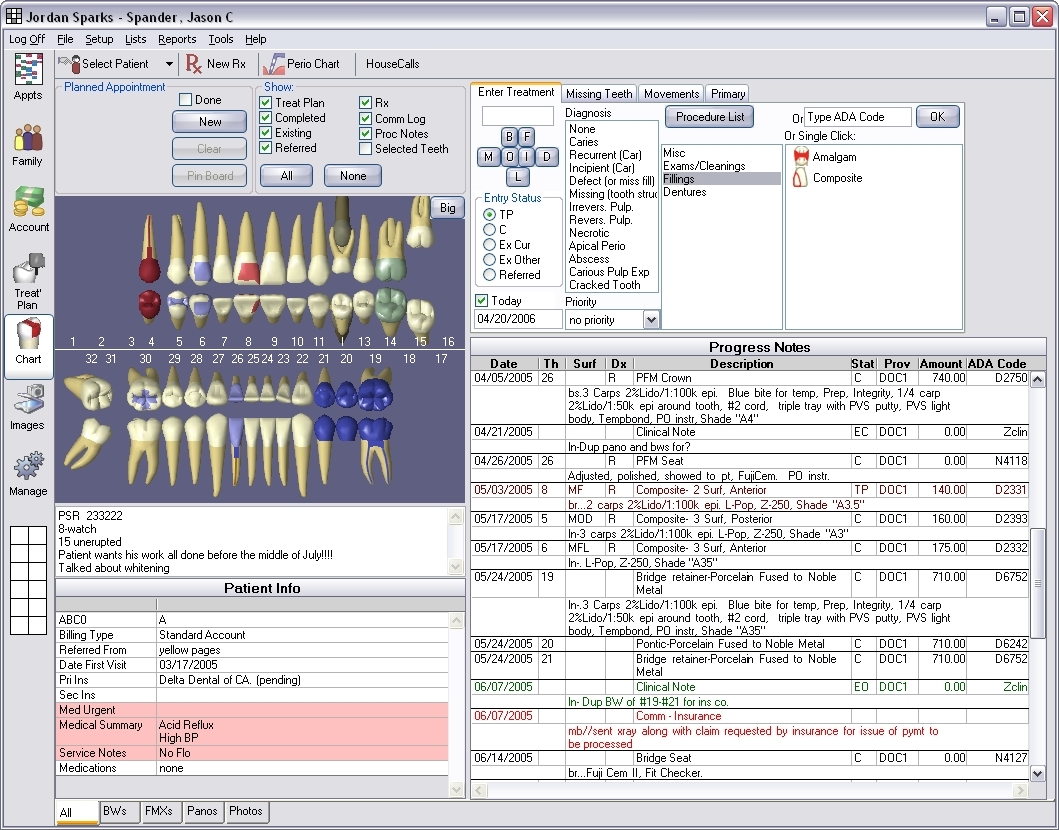 OpenDental is a Practice Management Software
OpenDental is a Practice Management SoftwareOpenDental boasts a powerful suite of features, including, but not limited to:
- OpenDental is designed to be used as a desktop software. There is no Web Version of Open Dental that will run in a browser by default. But some customization allows you to connect to Open Dental any time, anywhere using a supported internet browser and your mobile device;
- Medical Records (Patient records): name, contact info, insurance/billing data etc.;
- Scheduling: appointment calendar, color-coded entries, popup alerts, mass contact option etc.;
- E-prescribing: single/multiple drug prescription, printable patient instructions, audit trails etc.;
- Billing and claims management: invoice generation, billing template creation, claims validation and history etc.;
- Reporting: customizable insurance reports, accounting reports, evaluation reports, and more;
- Patient portal: customizable patient portal;
- Treatment plans: creation and management of single or multiple treatment plans, with changes in procedures reflecting in tooth charts;
- Charting: perio, ortho, 3D teeth charts integrated with prescribing, treatment plans and other modules;
- Medical image processing: integration with radiography, scanning, and digital cameras.
OpenDental is both ONC-certified and HIPAA-compliant, so its users are eligible for incentives under Promoting Interoperability program.
Being a popular tool for dentists, OpenDental has gathered a fair number of mostly positive user reviews (with a rating of 4,7/5 on Capterra), that are available to the general public. Among its advantages are:
- Professional and empathetic customer support;
- Customization options;
- Ease of use;
- Features that support all aspects of a dental practice;
- Regular improvements to the system.
However, the reviewers also mentioned a few flaws with this EHR:
- Steep learning curve;
- Lack of cloud deployment option;
- Scalability problems for large practices.
OpenDental is built with C# and a powerful .NET framework. This technology stack, endorsed by Microsoft, is very popular, so you won’t have to worry about the lack of professionals to support your system.
OpenDental is covered by GPL.
Rate this article
Recommended posts
Our Clients' Feedback

















.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)
















We have been working for over 10 years and they have become our long-term technology partner. Any software development, programming, or design needs we have had, Belitsoft company has always been able to handle this for us.
Founder from ZensAI (Microsoft)/ formerly Elearningforce